

Myomectomy is the surgical removal of fibroids from the uterus. It allows the uterus to be left in place and, for some women, makes pregnancy more likely than before. Myomectomy is the preferred fibroid treatment for women who want to become pregnant. After myomectomy, your chances of pregnancy may be improved but are not guaranteed.
Before myomectomy, shrinking fibroids with gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogue (GnRH-a) therapy may reduce blood loss from the surgery. GnRH-a therapy lowers the amount of estrogen your body makes. If you have bleeding from a fibroid, GnRH-a therapy can also improve anemiabefore surgery by stopping uterine bleeding for several months.
Surgical methods for myomectomy include:
The method used depends on the:
The length of time you may spend in the hospital varies.
Recovery time depends on the method used for the myomectomy:
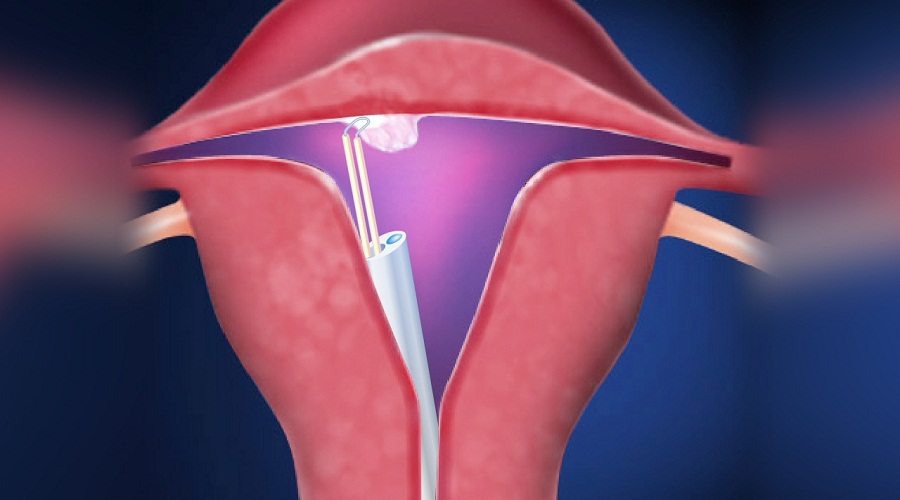
Myomectomy is the surgical removal of fibroids without removing the uterus.This can be performed through the abdominal wall, stomach or if the fibroids are small by laparoscope (a small tube inserted near the belly button) or hysteroscopy (a small tube is inserted through the vagina).
Myomectomy is normally only offered to women wishing to have children because most women will subsequently need to have a hysterectomy.
Myomectomy is a longer operation than hysterectomy, help often involving more bleeding. There is the considerable pain after the operation normally lasting from 3 to 10 days. The operation is associated with heavy bleeding requiring blood transfusions. A high fever occurs in a large proportion (32%) of patients.
Normal hospital stay is 6 days to 2 weeks.
Myomectomy is very invasive surgery. There is the danger of a hernia (protrusion of a portion of organ or tissue) if there is any lifting or stretching of the abdomen. For this reason, women must not even lift a kettle or drive a car for at least 6 weeks. Return to work is normally between 2 to 3 months, depending on the nature of the work.
Most women will need considerable care at home for at least 6 weeks because they will not be able to lift or stretch or drive. This means another member of the family will need to look after them.
Although myomectomy is effective at removing the fibroids in the short-term most re-grow and require further treatment. Adhesions, where surgically damaged tissues grow together and can cause severe pain occur in 55-100% of women. If a pregnancy occurs, the baby will normally be delivered by Caesarean section.
Fertility is maintained and if fibroids were the cause of infertility or miscarriage the success rate for pregnancies is high.